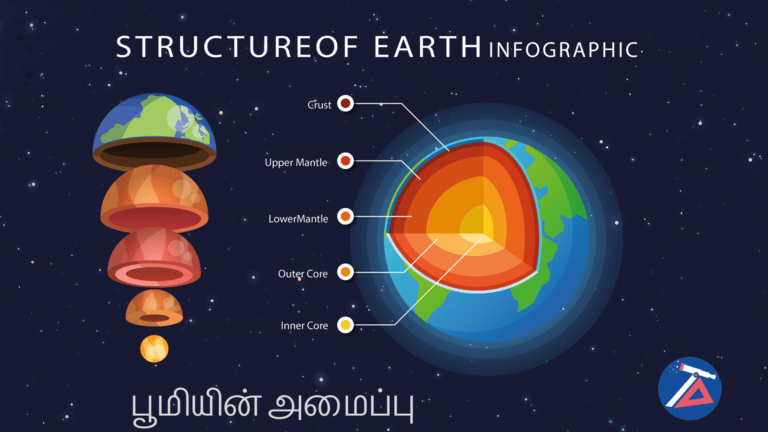
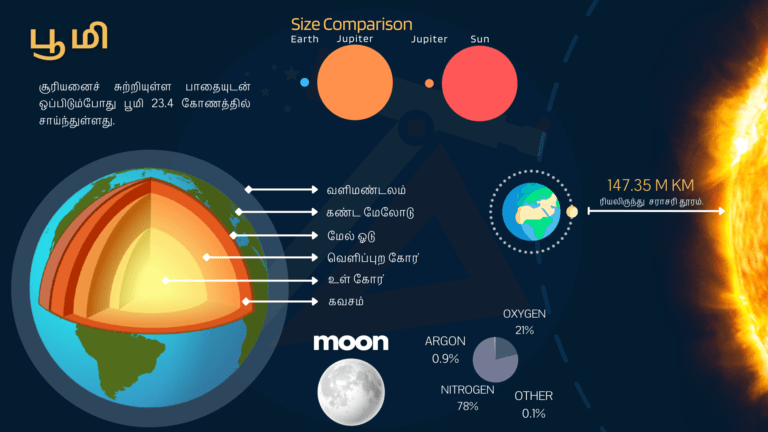
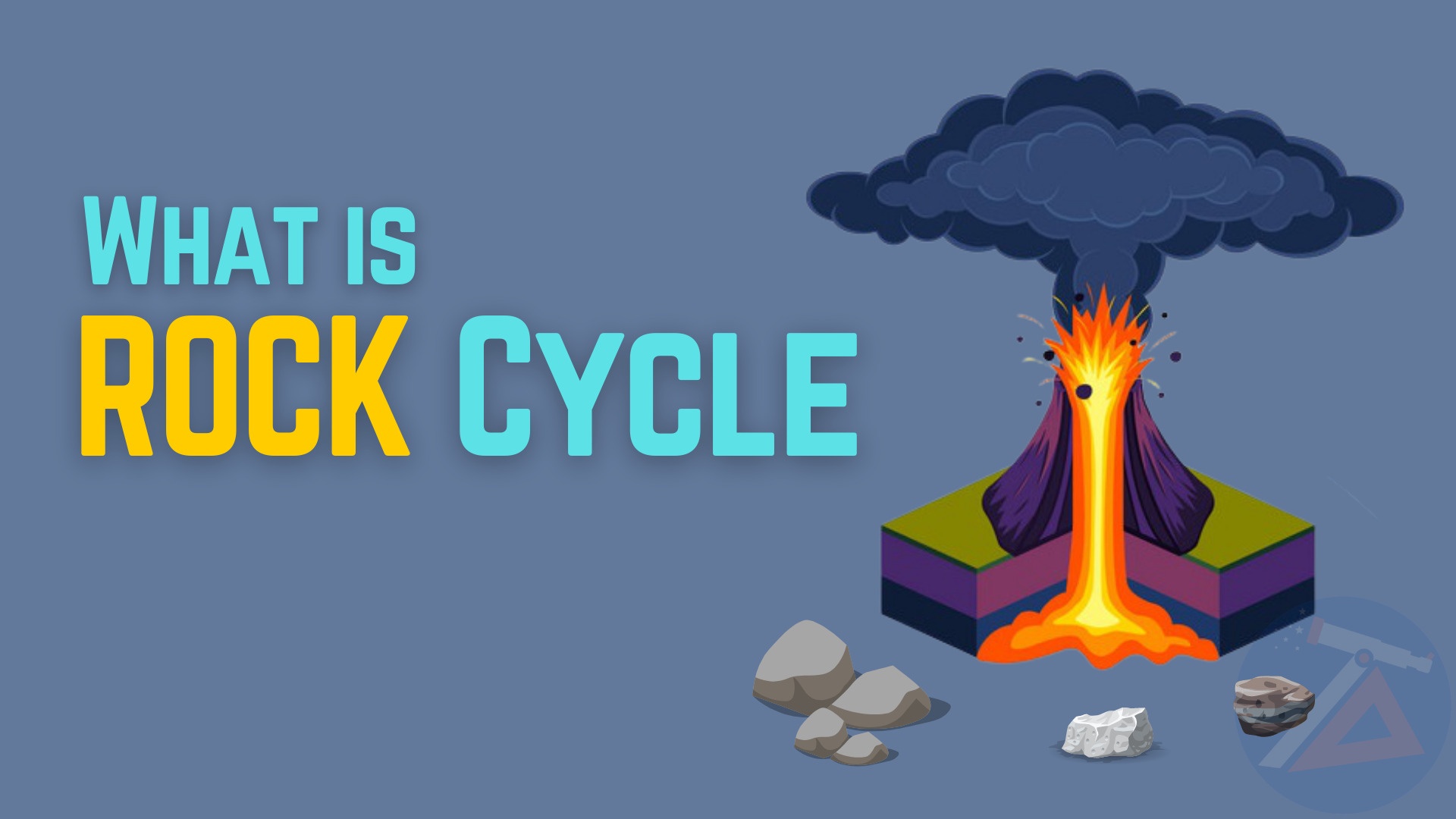
What is Rock Cycle? | பாறை சுழற்சி என்றால் என்ன?
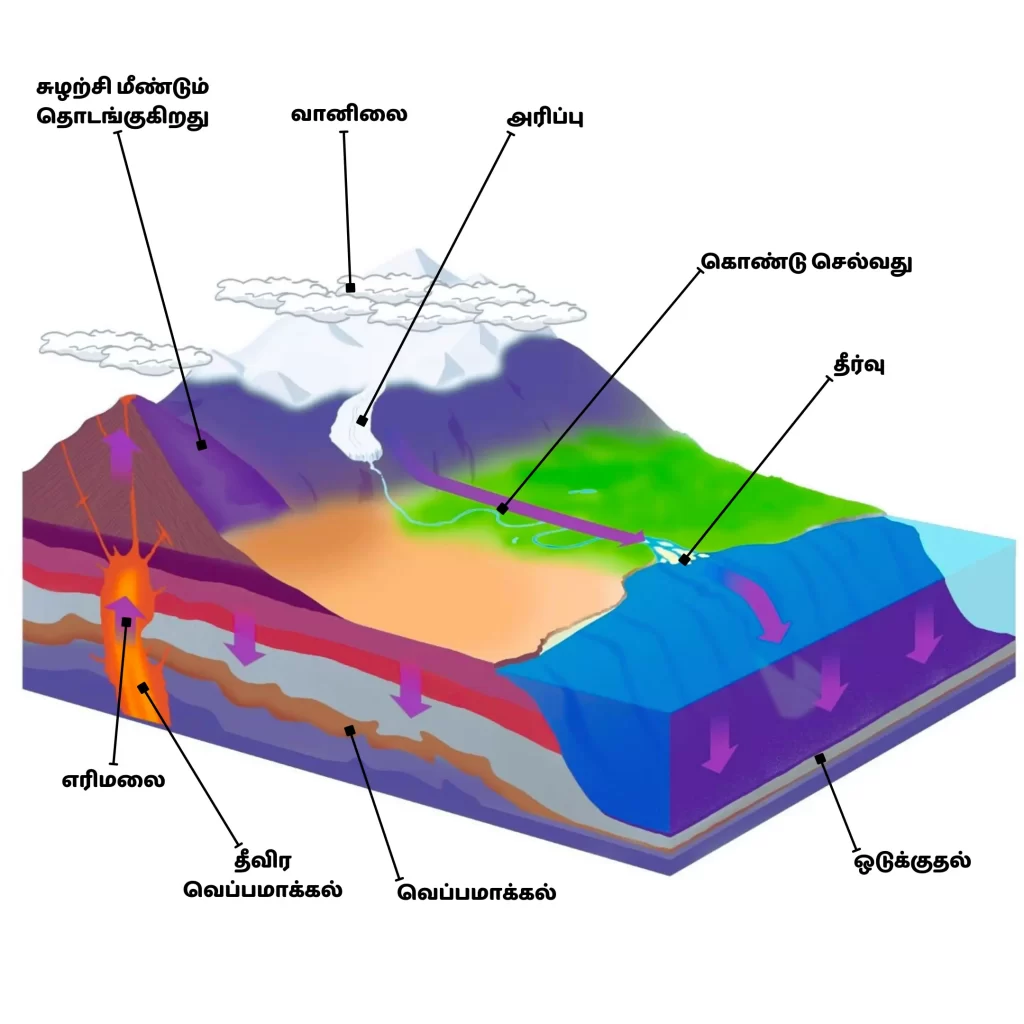
பாறை சுழற்சி
ஒரு பாறை சுழற்சி என்பது பூமியின் மேற்பரப்பில் இருந்து பாறைகளின் நீண்ட, மெதுவான பயணமாகும், பின்னர் மீண்டும் மேலே செல்கிறது. இந்த செயல்பாட்டின் போது பாறைகள் அடிக்கடி மாறுகின்றன.
பாறை சுழற்சி என்பது ஒரு முடிவற்ற செயல்முறையாகும், இதில் மில்லியன் கணக்கான ஆண்டுகளில் பாறைகள் மாறிக்கொண்டே இருக்கின்றன.
பாறை சுழற்சியின் போது, பாறைகள் பூமியில் ஆழமாக உருவாகின்றன, நகரும் மற்றும் சில நேரங்களில் மாறும், மேற்பரப்பு வரை சென்று இறுதியில் தரையில் திரும்பும்.
மூன்று முக்கிய பாறைகள் பற்றவைப்பு, வண்டல் மற்றும் உருமாற்றம். ஒவ்வொரு வகை பாறையும் வெவ்வேறு வழிகளில் சுழற்சியை நகர்த்துகிறது.
சுழற்சி மீண்டும் தொடங்குகிறது
வானிலை வழியாக எரிமலை பாறை அரித்து சுழற்சி மீண்டும் தொடங்குகிறது.
எரிமலை
மாக்மா (சூடான, திரவ பாறை) பூமியின் மேற்பரப்பில் எரிமலை வடிவில் வெடிக்கும். இது திடமான பாறையாக மாறும், இது இக்னியஸ் பாறை என்று அழைக்கப்படுகிறது.
வெப்பமாக்கல்
பூமியில் உள்ள ஆழமான வெப்பமும் அழுத்தமும் பாறை உருவாக்கம் வேறு வழியில் மாறலாம், இது உருமாற்ற பாறை என்று அழைக்கப்படுகிறது.
தீவிர வெப்பமாக்கல்
வெப்பம் அதிகமாக இருந்தால், வண்டல் மற்றும் உருமாற்ற பாறை இரண்டும் மிகவும் சூடாகும்போது மாக்மாவாக மாறும்.
தீர்வு
மணல், மண் அல்லது கூழாங்கற்களாக பாறைகள் கடற்கரையில் குடியேறுகின்றன. துண்டுகள் பின்னர் ஆறுகள் மூலம் கடலுக்குள் கொண்டு செல்லப்பட்டு மெதுவாக கடலின் அடிப்பகுதியில் குடியேறும்.
கொண்டு செல்வது
ஆறுகள் மற்றும் நீரோடைகள் பாறைத் துண்டுகளை எடுத்துச் செல்கின்றன, அதே நேரத்தில் அவற்றை மேலும் உடைக்கின்றன. பனிப்பாறைகள் (பனி மற்றும் பாறையின் பெரிய ஆறுகள்) மலைகளில் உள்ள பாறைகளை அகற்றி அவற்றை நீண்ட தூரம் கொண்டு செல்கின்றன.
அரிப்பு
அரிப்பு என்பது ஆறு, பனிப்பாறை அல்லது காற்று வழியாக பாறைத் துண்டுகளை நகர்த்துவது அல்லது எடுத்துச் செல்வதாகும்.
வானிலை
மழை, காற்று, உறைபனி, இரசாயனங்கள், வெப்பம் மற்றும் உயிரினங்கள் அனைத்தும் பாறைகளை உடைக்கின்றன.
சுருக்கம்
ஒரு கடல் அல்லது ஏரியின் அடிப்பகுதியில் உள்ள பாறை துண்டுகள் நசுக்கப்பட்டு ஒன்றாக பிணைக்கப்பட்டுள்ளன. அவை படிப்படியாக கடினமாகி திடமான வண்டல் பாறையை உருவாக்குகின்றன.
பாறை சுழற்சி எப்படி வேலை செய்கிறது?
முடிவில்லாத சுழற்சியில் பாறைகள் ஒரு வகையிலிருந்து இன்னொரு வகைக்கு மாறும். பூமியின் மேற்பரப்பிலும் அதன் உட்பகுதியிலும் இந்த செயல்முறைக்கு பல காரணிகள் பங்களிக்கின்றன.
மேற்பரப்பில், காற்று அல்லது மழை போன்ற வானிலை காரணமாக பாறை உடைகிறது. பனிப்பாறைகள் மற்றும் ஆறுகள் பாறைகளை அரிக்கின்றன. பாறைகளின் சிறிய துகள்களால் உருவாகும் வண்டல் மற்றும் கடற்கரைகள், கடல்கள் மற்றும் ஏரிகளின் அடிப்பகுதி போன்ற இடங்களில் மண் உருவாகிறது.
பூமியின் உள்ளே, வெப்பம், அழுத்தம் மற்றும் உருகுதல் வண்டல் மற்றும் எரிமலை பாறையை உருமாற்ற பாறையாக மாற்றுகிறது. தீவிர வெப்பமயமாதல் பூமியின் மேற்பரப்பில் சூடான திரவ பாறை (மாக்மா) வெடித்து திட எரிமலை பாறையாக மாறும்.
காலப்போக்கில், இந்த பாறை வானிலை மற்றும் அரிப்பு ஏற்படுகிறது, மற்றும் சுழற்சி மீண்டும் தொடங்குகிறது.
English Version
Rock Cycle
A rock cycle is a long, slow journey of rocks from the Earth’s surface, then ascending again. The rocks change frequently during this process.
Rock Cycle is an endless process in which rocks change over millions of years.
During Rock Cycle, rocks from deep in the earth, moving and sometimes changing, go up to the surface and eventually return to the ground.
The three main rocks are ignition, sediment, and metamorphosis. Each type of rock moves in the cycle in different ways.
The cycle begins again
Through the weather, the eruption of the volcanic rock begins again.
Volcano
Magma (hot, liquid rock) erupts in the form of volcanoes on the Earth’s surface. It turns into solid rock, which is called Igneous rock.
Heating
Deep heat and pressure on Earth can cause rock formation to change in a different way, which is called metamorphic rock.
Intense heating
If the heat is too high, both the sediment and the metamorphic rock will turn into magma when it gets too hot.
Solution
Rocks settle on the beach as sand, mud or pebbles. The fragments are then carried into the sea by rivers and slowly settle to the bottom of the ocean.
Carrying
Rivers and streams carry pieces of rock and at the same time break them further. Glaciers (large rivers of ice and rock) remove rocks in the mountains and carry them long distances.
Erosion
Erosion is the movement or carrying of pieces of rock through a river, glacier, or wind.
Weather
Rain, wind, frost, chemicals, heat, and organisms all break rocks.
Summary
Rock fragments at the bottom of a sea or lake are crushed and bound together. They gradually harden and form solid sedimentary rock.
How does the rock cycle work?
In an endless cycle, the rocks change from one type to another. Many factors contribute to this process on the earth’s surface and in its interior.
At the surface, the rock breaks due to weather such as wind or rain. Glaciers and rivers erode rocks. Sediment is formed by small particles of rock and soil is formed at the bottom of beaches, seas, and lakes.
Inside the Earth, heat, pressure, and melting transform sediment and volcanic rock into metamorphic rock. Extreme warming causes the hot liquid rock (magma) to erupt on the Earth’s surface and turn into solid volcanic rock.
Over time, this rock weather and erosion occurs, and the cycle begins again.