Asteroid 4179 Toutatis | சிறுகோள் 4179 Toutatis

Toutatis சிறுகோள்
சுற்றுப்பாதை காலம்: 1,471 நாட்கள்
ஆரம்: 1.225 கி.மீ
நிறை: 50.5 டிரில்லி
கண்டுபிடித்தவர்: கிறிஸ்டியன் பொல்லாஸ்
கண்டுபிடிக்கப்பட்ட நாள்: 4 ஜனவரி 1989
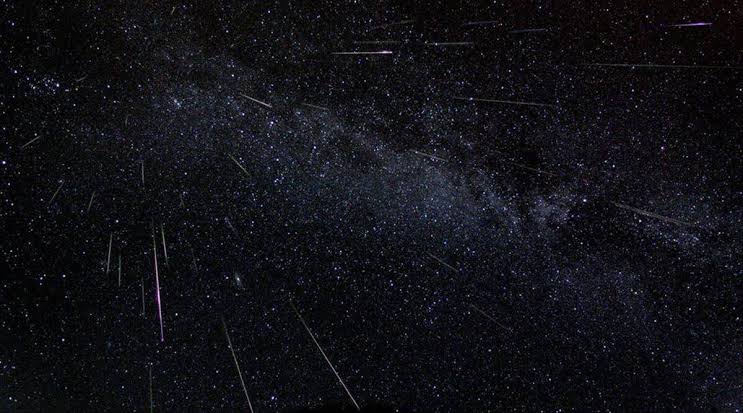
1989 இல், பிரெஞ்சு வானியலாளர் Christian Pollas 3-மைல்- (5-கிமீ-) அகலமான 4179 Toutatis என்ற சிறுகோளைக் கண்டுபிடித்தார்.
இது மேலே உள்ள கலைஞரின் தோற்றத்தில் காட்டப்பட்டுள்ளது. Toutatis பூமிக்கு அருகில் உள்ள சிறுகோள் ஆகும், அதாவது அதன் சுற்றுப்பாதை சில நேரங்களில் பூமிக்கு அருகில் கொண்டு வருகிறது.
2004 இல் பூமியைக் கடந்த போது, அது சந்திரனை விட நான்கு மடங்கு தொலைவில் இருந்தது.
20 மில்லியன் ஆண்டுகளுக்கு ஒருமுறை Toutatis போன்ற பெரிய சிறுகோள்கள் பூமியைத் தாக்கும். ஆனால், ஒட்டுமொத்த உலக மக்களையும் அழித்துவிடும் ஆற்றல் கொண்டது.
 Toutatis இன் வடிவம், ஒட்டிக்கொண்ட இரண்டு சிறுகோள்களிலிருந்து உருவாகியிருக்கலாம் என்று கூறுகிறது?
Toutatis இன் வடிவம், ஒட்டிக்கொண்ட இரண்டு சிறுகோள்களிலிருந்து உருவாகியிருக்கலாம் என்று கூறுகிறது?
ஒன்றாக, ஒரு சிறிய சிறுகோள் “தலை” (இடது) மற்றும் பெரிய ஒன்று உடலை உருவாக்குகிறது.
பெரும்பாலான சிறுகோள்கள் ஒழுங்கற்ற வடிவத்தைக் கொண்டுள்ளன, ஆனால் மிகப் பெரியவை அவற்றின் சொந்த ஈர்ப்பு விசையின் மூலம் ஒரு கோளத்திற்குள் இழுக்கின்றன.
பள்ளங்கள்
சிறுகோள்கள் சிறிய சிறுகோள்களுடன் மோதுவதால் ஏற்படும் பள்ளங்களால் குறியிடப்படுகின்றன.
நெருங்கிய அணுகுமுறைகள் (Close approaches)
| YEAR | 1985 | 1988 | 1992 | 1996 | 2000 | 2004 | 2008 | 2012 | 2016 | 2065 | 2069 |
| AU | 0.28 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.36 | 0.02 |
சிறுகோள்கள் (Small Facts)
சிறுகோள்கள் எனப்படும் மில்லியன் கணக்கான பாறைகள் உள் சூரிய குடும்பத்தைச் சுற்றி வருகின்றன, அவை கூழாங்கற்கள் முதல் நூற்றுக்கணக்கான மைல்கள் அகலமுள்ள அரக்கர்கள் வரை இருக்கும்.
அவற்றில் பெரும்பாலானவை செவ்வாய் மற்றும் வியாழனின் சுற்றுப்பாதைகளுக்கு இடையில் ஒரு பெல்ட்டில் உள்ளன.
சிறுகோள்கள் (Asteroids) என்பது கோள்களுக்குக் காரணமான இடிந்த மேகத்தில் இருந்து எஞ்சியவை. உள் சூரிய குடும்பத்தில் உள்ள பெரும்பாலான இடிபாடுகள் ஒன்றாக சேர்ந்து பாறைக் கோள்களாக மாறியது.
ஆனால் வியாழனுக்கு அருகிலுள்ள பாறைகள் ராட்சத கிரகத்தின் ஈர்ப்பு விசையால் தொந்தரவு செய்யப்பட்டு, உருவாக்கத் தவறிவிட்டன.
சிறுகோள் பெல்ட் என்பது அந்த குப்பைகளில் இன்று எஞ்சியுள்ளது. சிறுகோள்கள் சூரியனைச் சுற்றி அவற்றின் சொந்த சுற்றுப்பாதையைப் பின்பற்றுகின்றன, அவை கிரகங்களைப் போல சுழல்கின்றன.
அவை சிறிய கிரகங்கள் என்றும் அழைக்கப்படுகின்றன, மேலும் அனைத்திலும் மிகப்பெரிய சிறுகோள், செரெஸ், ஒரு குள்ள கிரகமாக வகைப்படுத்தப்பட்டுள்ளது.
சிறுகோள்கள் அவ்வப்போது மோதுகின்றன, பள்ளங்களை உருவாக்குகின்றன அல்லது ஒன்றையொன்று நொறுக்குகின்றன. குறைவாக அடிக்கடி, அவை நிலவுகள் மற்றும் கிரகங்களில் மோதுகின்றன.
சிறுகோள் பெல்ட்
பெரும்பாலான சிறுகோள்கள் செவ்வாய் மற்றும் வியாழனின் சுற்றுப்பாதைகளுக்கு இடையில் ஒரு டோனட் வடிவ பெல்ட்டில் உள்ளன.
ஆனால் உள் கிரகங்களில் சிதறிய சிறுகோள்கள் மற்றும் அதே சுற்றுப்பாதையில் உள்ள சிறுகோள்களின் பெரிய குழுக்களும் உள்ளன. வியாழன், ட்ரோஜான்கள் என அறியப்படுகிறது. பெல்ட் அடிக்கடி கூட்டமாக தெரிகிறது.
சிறுகோள்கள் வெகு தொலைவில் இருப்பதால் சிறுகோள் பெல்ட் வழியாக ஒரு விண்கலத்தில் பயணிப்பவர்கள் ஒரு சிறுகோள் கூட பார்க்க மாட்டார்கள்.
பெல்ட்டில் உள்ள அனைத்து சிறுகோள்களின் மொத்த நிறை சந்திரனின் நிறைவில் 4 சதவீதம் மட்டுமே கொண்டுள்ளது.
அளவு
பெரிய சிறுகோள்கள் மிகவும் அரிதானவை – 26 சிறுகோள்கள் மட்டுமே 125 மைல்கள் (200 கிமீ) அகலம் கொண்டதாக அறியப்படுகிறது.
இருப்பினும், நூறாயிரக்கணக்கான சிறுகோள்கள் 0.6 மைல்கள் (1 கிமீ) மற்றும் மில்லியன் கணக்கான சிறியவை.
பூமிக்கு அருகில் உள்ள சிறுகோள்கள்
கடந்த காலங்களில், சிறுகோள்கள் பூமியைத் தாக்கியதால், டைனோசர்கள் உட்பட ஏராளமான விலங்குகள் அழிக்கப்பட்டன.
இன்று, வானியலாளர்கள் நமது கிரகத்திற்கு அருகில் சுற்றித் திரியும் சிறுகோள்களை உன்னிப்பாகக் கவனித்து வருகின்றனர்.
பூமிக்கு அருகில் சுமார் 12,000 சிறுகோள்கள் கண்டுபிடிக்கப்பட்டுள்ளன, அவற்றில் சுமார் 1,000 “0.6 மைல்கள்” (1 கிமீ) அகலம் கொண்டவை – ஒரு பெரிய நகரத்தின் அளவு பள்ளத்தை உருவாக்கும் அளவுக்கு பெரியவை.
English Version
Toutatis asteroid
Orbital period: 1,471 days
Radius: 1.225 km
Weight: 50.5 trillion
Invented by: Christian Pollas
Date of discovery: 4 January 1989
In 1989, French astronomer Christian Pollas discovered the asteroid 4179 Toutatis, which is 3 miles (5 km) wide.
This is shown in the appearance of the artist above. Toutatis is the closest asteroid to Earth, meaning its orbit is sometimes brought closer to Earth.
When it crossed the Earth in 2004, it was four times farther away than the Moon.
 Large asteroids like Toutatis will hit Earth once every 20 million years. But has the power to destroy the entire population of the world.
Large asteroids like Toutatis will hit Earth once every 20 million years. But has the power to destroy the entire population of the world.
Says the shape of the Toutatis may have evolved from two sticking asteroids?
Together, a small asteroid forms the “head” (left) and the larger one the body.
Most asteroids have an irregular shape, but the largest are pulled into a sphere by their own gravitational pull.
Grooves
Asteroids are coded by craters caused by collisions with smaller asteroids.
Close approaches
| YEAR | 1985 | 1988 | 1992 | 1996 | 2000 | 2004 | 2008 | 2012 | 2016 | 2065 | 2069 |
| AU | 0.28 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.25 | 0.36 | 0.02 |
Asteroids (Small Facts)
Millions of rocks called asteroids to orbit the inner solar system, ranging from pebbles to monsters hundreds of miles wide.
Most of them are in a belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
Asteroids are remnants of the cloud that caused the planets. Most of the debris in the inner solar system came together to form rocky planets.
But the rocks near Jupiter were disturbed by the gravitational pull of the giant planet and failed to form.
The asteroid belt is what remains of that debris today. Asteroids follow their own orbits around the Sun, which orbit like planets.
They are also called asteroids, and the largest of all asteroids, Ceres, is classified as a dwarf planet.
Asteroids collide from time to time, forming craters or colliding with each other. Less often, they collide with moons and planets.
Asteroid belt
Most asteroids are in a donut-shaped belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
But there are scattered asteroids on the inner planets and large groups of asteroids in the same orbit. Jupiter, also known as the Trojans. The belt often seems crowded.
Because the asteroids are so far away, those who travel in a spacecraft through the asteroid belt will not even see an asteroid.
The total mass of all the asteroids in the belt is only 4 percent of the lunar mass.
Size
Large asteroids are extremely rare – only 26 asteroids are known to be 125 miles (200 km) wide.
However, hundreds of thousands of asteroids are 0.6 miles (1 km) and millions smaller.
Asteroids close to Earth
In the past, numerous animals, including dinosaurs, have been wiped out by asteroids.
Today, astronomers are closely monitoring asteroids orbiting our planet.
About 12,000 asteroids have been discovered near-Earth, about 1,000 “0.6 miles” (1 km) wide – large enough to form the size of a large city.