Compared to Earth’s atmosphere with Mars.
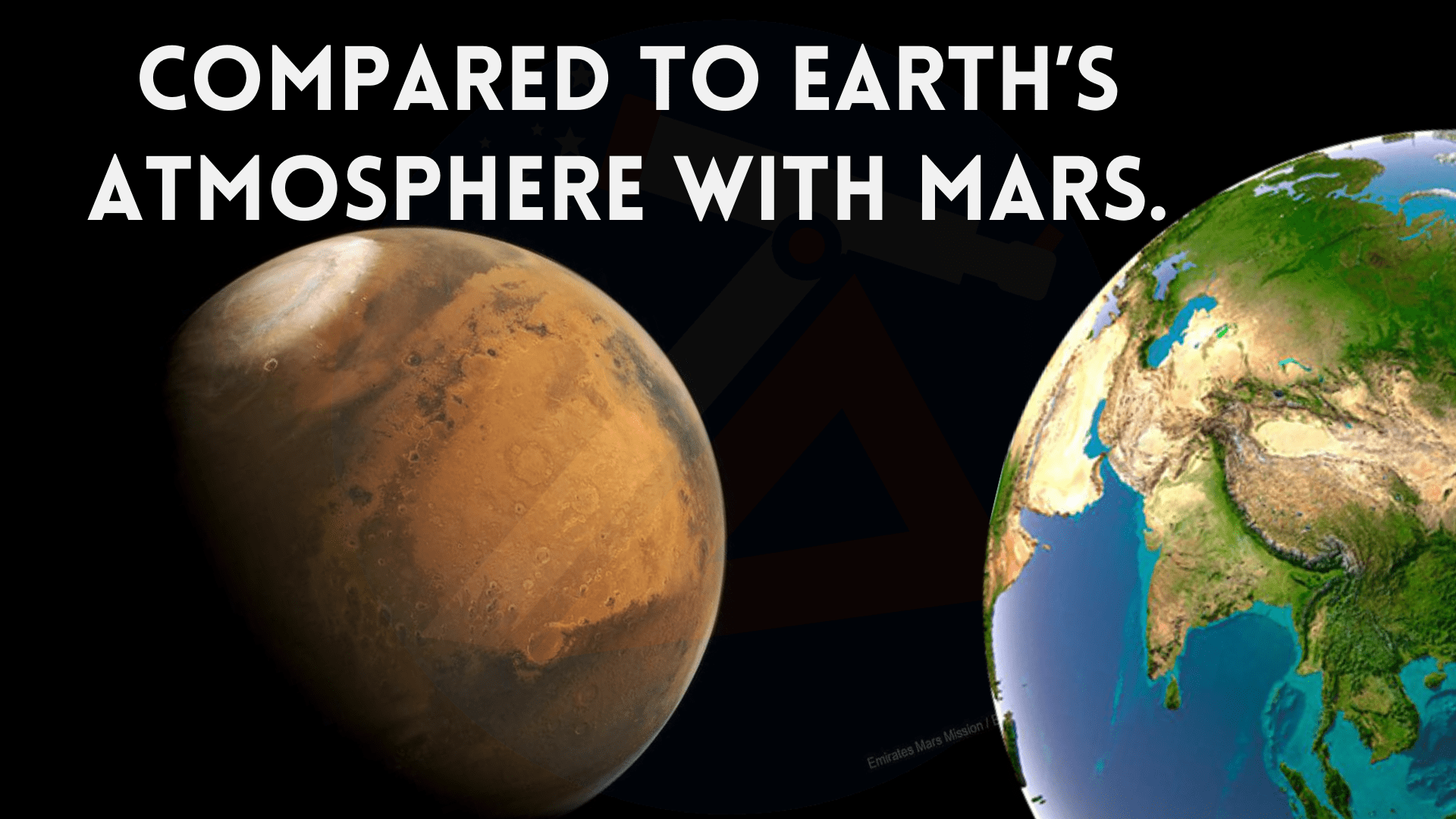
செவ்வாய் கிரகத்துடன் பூமியின் வளிமண்டலத்துடன் ஒப்பிடும்போது.
செவ்வாய் கிரகத்தின் வளிமண்டலம் பெரும்பாலும் கார்பன் டை ஆக்சைடை அடிப்படையாகக் கொண்டது. ஆனால் பூமியின் வளிமண்டலத்தில் நைட்ரஜன் மற்றும் ஆக்ஸிஜன் நிறைந்துள்ளது. கீழே உள்ள அட்டவணையில் அவற்றின் வளிமண்டல கலவைகளை நீங்கள் ஒப்பிடலாம்:
| வாயுக்கள் | Mars | Earth |
| Carbon dioxide (CO2) | 96% | 0.0391% |
| Nitrogen | 1.9% | 78.1% |
| Oxygen | 0.174% | 20.9% |
| Argon | 1.9% | 0.93% |
வீனஸைப் போலவே, செவ்வாய் கிரகத்திலும் கார்பன் டை ஆக்சைடு ஆதிக்கம் செலுத்துகிறது. அதிர்ஷ்டவசமாக, CO2 பூமியின் வளிமண்டலத்தில் 1% க்கும் குறைவாக உள்ளது. செவ்வாய் கிரகத்தின் வளிமண்டலத்தில் 96% கார்பன் டை ஆக்சைடு உள்ளது.
பூமியின் வளிமண்டலத்தில் 78.1% நைட்ரஜன் என்றாலும், செவ்வாய் 1.9% நைட்ரஜனை அடிப்படையாகக் கொண்டது. பூமியில் ஆக்ஸிஜன் (20.9%) நிறைந்துள்ளது. ஆனால் செவ்வாய் கிரகத்தில் ஆக்ஸிஜனின் மிக குறைந்த அளவை மட்டுமே பார்க்க முடியும். சுவடு வாயுக்களைத் தவிர்த்து, செவ்வாய் கிரகத்தின் வளிமண்டலத்தில் 1.9% ஆர்கான் உள்ளது.
செவ்வாய் வளிமண்டலத்தின் அளவு பூமியிலிருந்து எவ்வாறு வேறுபடுகிறது?
பூமியுடன் ஒப்பிடும்போது செவ்வாய் வளிமண்டல அளவு மிகவும் மெல்லியதாக உள்ளது. பூமியின் வளிமண்டலம் செவ்வாய் கிரகத்தை விட 100 அடர்த்தியானது.
மேலே உள்ள விளக்கப்படத்தில் பூமியின் அளவு செவ்வாய் கிரகத்துடன் ஒப்பிடும்போது மிகவும் பெரியது என்பதை நினைவில் கொள்ளுங்கள். செவ்வாய் கிரகத்தின் விட்டம் பூமியின் பாதி அளவு உள்ளது.
மொத்த வெகுஜனத்தை நீங்கள் கணக்கிட்டால், செவ்வாய் பூமியின் 10% ஆகும். அளவைப் பொறுத்தவரை, பூமியை நிரப்ப 6 செவ்வாய் தேவைப்படும்.
செவ்வாய் கிரகத்தின் வளிமண்டலத்தின் வரலாறு என்ன?
செவ்வாய் கிரகத்தின் வளிமண்டலம் ஒரு காலத்தில் மிகவும் வெப்பமாகவும் ஈரப்பதமாகவும் இருந்தது என்பதற்கு ஏராளமான சான்றுகள் உள்ளன.
செவ்வாய் கிரகத்தில் காந்தப்புலம் இல்லாததால், சூரியக் காற்று செவ்வாய் கிரகத்தின் வளிமண்டலத்தின் பெரும்பகுதியை குளிர்ந்த, வறண்ட செவ்வாய் கிரகமாக மாற்றியுள்ளது.
மேலும், செவ்வாய் கிரகத்தில் தூசி புயல்கள் உள்ளன, அவை முழு கிரகத்தையும் உள்ளடக்கியது மற்றும் வாரங்களுக்கு நீடிக்கும். இந்த தூசி புயல்கள் வளிமண்டல வெப்பநிலையை மாற்றும் அளவுக்கு உள்ளன.
செவ்வாய் கிரகத்தில் உள்ள சுவடு வாயுக்கள் என்ன?
செவ்வாய் கிரகத்தில் உள்ள சுவடு வாயுக்கள் செவ்வாய் கிரகத்தின் அளவின் 1% க்கும் குறைவாகவே உள்ளன. அவை பின்வரும் வாயுக்களைக் கொண்டிருக்கின்றன – Acetylene, Carbon monoxide, Krypton, Methane, Neon, Nitrogen oxide, Oxygen, Ozone, Water vapor, மற்றும் xenon.
அவை ஒரு சிறிய சதவீத அளவாக இருந்தாலும், ESA இன் எக்ஸோமார்ஸ் டிரேஸ் கேஸ் ஆர்பிட்டர் ( ESA’s ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter) இந்த வகையான சுவடு வாயுக்களை முகர்ந்து பார்க்கும் திறன் கொண்டது.
குறிப்பாக, செவ்வாய் கிரகத்தின் வளிமண்டலத்தில் உள்ள மீத்தேன் அளவு செவ்வாய் கிரகத்தின் கடந்த கால வளிமண்டலத்திற்கான தடயங்களைக் கொண்டுள்ளது.
பூமியில், வளிமண்டலத்தில் மீத்தேன் வெளியிடப்படுவது பெரும்பாலும் கால்நடைகள் மற்றும் பிற விவசாய நடைமுறைகள் காரணமாகும். இருப்பினும், ஹைட்ரோகார்பன் வாயு தேக்கங்கள் மற்றும் எரிமலை செயல்பாடுகள் மீத்தேன் வெளியிடலாம்.
வளிமண்டலத்தில் மீத்தேன் வெளியிடுவதில் உயிரியல் முக்கிய பங்கு வகிப்பதால், அதன் ஆதாரம் ESA இன் Mars Exploration Program முதன்மையானது.
Compared to Earth’s atmosphere with Mars.
Mars’ atmosphere is largely based on carbon dioxide. But the Earth’s atmosphere is rich in nitrogen and oxygen. You can compare their atmospheric compositions in the table below:
| வாயுக்கள் | Mars | Earth |
| Carbon dioxide (CO2) | 96% | 0.0391% |
| Nitrogen | 1.9% | 78.1% |
| Oxygen | 0.174% | 20.9% |
| Argon | 1.9% | 0.93% |
Like Venus, Mars is dominated by carbon dioxide. Fortunately, CO2 is present in less than 1% of the Earth’s atmosphere. Mars’ atmosphere contains 96% carbon dioxide.
Although 78.1% of the Earth’s atmosphere is nitrogen, Mars is based on 1.9% nitrogen. Earth is rich in oxygen (20.9%). But only very low levels of oxygen can be seen on Mars. Excluding trace gases, Mars’ atmosphere contains 1.9% argon.
How does the size of the Mars atmosphere differ from that of Earth?
The Mars atmosphere is very thin compared to Earth. Earth’s atmosphere is 100 times denser than Mars’. Note that the size of the Earth in the chart above is very large compared to Mars. The diameter of Mars is half the size of Earth.
If you calculate the total mass, Mars is 10% of Earth. In terms of size, it would take 6 Mars to fill the Earth.
What is the history of the atmosphere of Mars?
There is ample evidence that the atmosphere of Mars was once very hot and humid. Due to the absence of a magnetic field on Mars, the solar wind has transformed much of Mars’ atmosphere into cold, dry Mars.
Also, there are dust storms on Mars that cover the entire planet and can last for weeks. These dust storms are capable of changing atmospheric temperature.
What are the trace gases on Mars?
The trace gases on Mars are less than 1% of the size of Mars. They contain the following gases – Acetylene, Carbon monoxide, Krypton, Methane, Neon, Nitrogen oxide, Oxygen, Ozone, Water vapor, and xenon.
Although they are a small percentage, ESA’s ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter is capable of sniffing out these types of trace gases. In particular, the amount of methane in Mars ‘atmosphere contains traces of Mars’ past atmosphere.
On Earth, the release of methane into the atmosphere is largely due to livestock and other agricultural practices. However, hydrocarbon gas reservoirs and volcanic activity can release methane.
Because biology plays an important role in the release of methane into the atmosphere, its source is ESA’s Mars Exploration Program.






